The Ultimate Guide to Resin 3D Printer Printing Material

When a vat of clear liquid resin gradually solidifies under ultraviolet light, transforming into intricately detailed objects, it represents more than just manufacturing—it’s an artistic spectacle where material and light perform in perfect harmony. Resin 3D printing, the modern craft that transforms digital concepts into tangible reality, is redefining the boundaries of fabrication with its unique appeal.
Resin 3D printer material selection becomes a profound dialogue that shapes the very essence of the final product. Each resin material possesses its own distinct characteristics: some are remarkably durable, ready to bear significant loads; others are smooth and elegant, perfect for display purposes; while still others are specially formulated for unique applications. Just as sculptors understand marble grain and painters master pigment properties, truly commanding resin 3D printing requires a deep understanding of how these liquid materials transform under light’s magic. Let’s embark on this exploration journey together, uncover the mysteries of various resin materials, and discover the key to perfectly realizing your creative visions.
Understanding Resin 3D Printing Technology
Resin 3D printing, also known as photopolymerization or SLA technology, uses specific wavelength light sources to cure liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer, creating parts with precision reaching tens of microns. Compared to traditional Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) technology, resin printing offers significant advantages in detail reproduction and surface smoothness, making it particularly suitable for high-precision models and components.
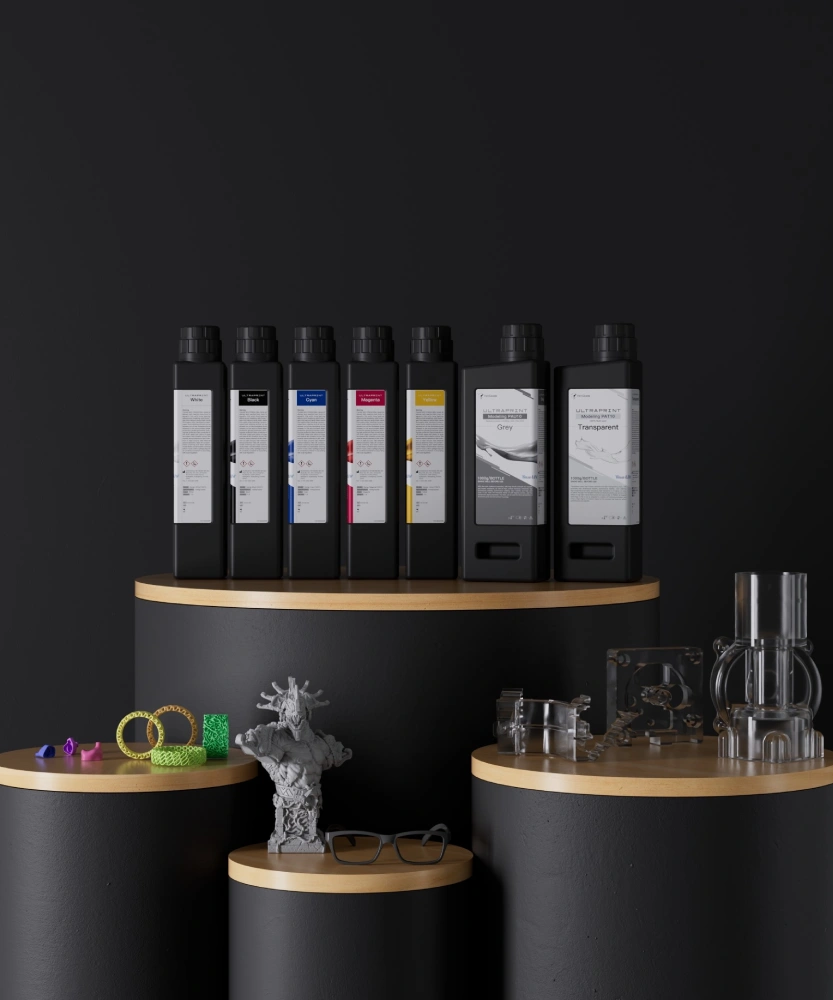
Comprehensive Analysis of Resin Material Categories
Standard Resins
As the most fundamental resin material, standard resins for resin 3D printers serve as the entry point for beginners with their affordable price and colour variety. Models printed with these materials feature smooth surfaces suitable for concept models, display props, and visual verification. However, these materials tend to be brittle with generally modest mechanical properties, making them unsuitable for functional parts requiring load-bearing capacity.
Engineering Resins
- High-Toughness Resins: Offer excellent impact resistance and fatigue endurance, with performance comparable to traditional ABS or PP engineering plastics. Ideal for functional prototypes, snap-fit components, and equipment housings that need to withstand certain stress levels.
- Rigid Resins: Distinguished by exceptional hardness, bending resistance, and dimensional stability, along with good heat and chemical resistance. Commonly used for manufacturing jigs, fixtures, electronic enclosures, and other structural components requiring shape precision.
- High-Temperature Resins: Feature heat deflection temperatures exceeding 200°C, maintaining structural stability in high-temperature environments. Perfect for thermal fluid testing, engine components, and casting moulds.
Special Application Resins
- Biocompatible Resins: Certified for biological safety, suitable for safe human contact, widely used in surgical guides, dental models, and hearing aid applications in medical fields.
- Castable Resins: Specifically designed for jewelry casting, with minimal ash residue after burning, perfectly replacing traditional wax patterns. An invaluable tool for jewelry designers.
- Elastomers: Exhibit rubber-like elasticity, capable of withstanding repeated bending and compression. Suitable for soft robotics components, consumer product prototypes, and special effects props.
Post-Processing and Safety Protocols
Successful resin 3D printing depends not only on the printing process itself but also on proper post-processing and safety management.
The complete printing workflow involves three crucial steps:
Printing → chemical cleaning, → UV curing.
Thoroughly cleaning model surfaces with chemicals like isopropyl alcohol to remove uncured resin residue is essential for ensuring print quality, while subsequent UV curing provides the material with its final mechanical properties.
Safety must be emphasized: uncured resin may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions. Always work in well-ventilated areas and wear appropriate protective equipment, including nitrile gloves and safety goggles.
See also: How to Create Perfect Chamfered Corners: Tips and Techniques
Equipment Recommendation: HeyGears UltraCraft Series
In a variety of resin 3D printers, the HeyGears Reflex series resin 3D printer deserves attention. These printers feature highly integrated intelligent systems with advanced functions, including automatic material recognition, precise level control, and one-click calibration, significantly simplifying operational processes and improving printing success rates.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate resin material is crucial for successful 3D printing. Whether you’re an artist pursuing extreme detail, an engineer requiring functional testing, in professional manufacturing, everyone can find the most suitable solution among the rich variety of resin materials. As material science continues to advance, resin 3D printing will undoubtedly demonstrate its unique value across more fields, helping transform creative concepts into reality.
Resin 3D Printing Material Selection FAQ
Q1: What type of resin should I use for parts that need to bear loads or withstand impact?
A: For load-bearing or impact-resistant parts, we recommend using high-toughness resins or rigid resins. These materials offer excellent mechanical properties, with high-toughness resins providing outstanding impact resistance and fatigue endurance, while rigid resins maintain exceptional dimensional stability under stress.
Q2: Which resin material is suitable for high-temperature environments?
A: If your parts will be exposed to high-temperature conditions, high-temperature resins are the ideal choice. These specialized materials can withstand temperatures exceeding 200°C while maintaining structural integrity, making them perfect for thermal testing, engine components, and other high-heat applications.
Q3: What resin should I select for medical applications involving human contact?
A: For any applications requiring human contact or implantation, you must use certified biocompatible resins. These materials have undergone rigorous testing and meet relevant biological safety standards, ensuring they’re safe for use in surgical guides, dental models, and other medical applications.
Q4: Which resin is most cost-effective for display models and visual prototypes?
A: For display-only purposes and visual prototypes, standard resins provide the best cost-effectiveness. They offer good surface quality and colour variety at an affordable price point, making them ideal for concept models, presentation pieces, and visual verification projects.