How Reliable Are Polygraph Tests in Georgia?
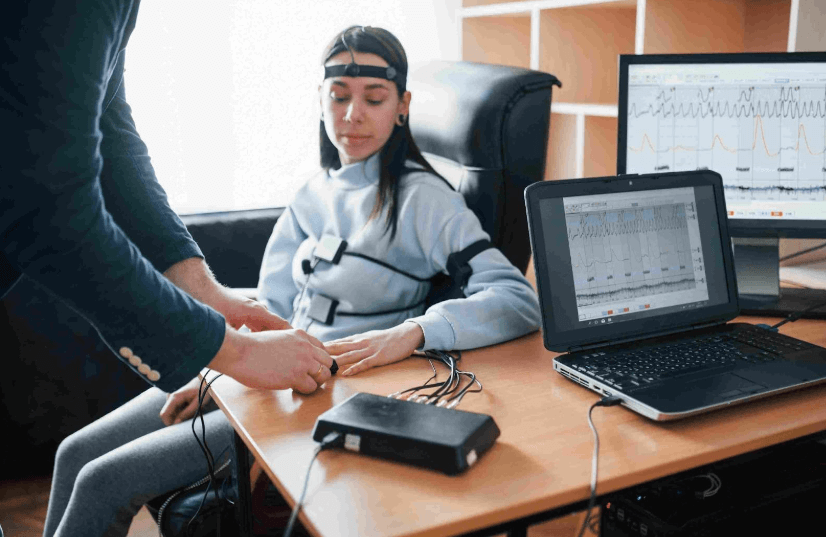

Polygraph tests, commonly known as lie detector tests, have long been a subject of fascination and controversy. In Georgia, as in many other states, the use of polygraphs spans criminal investigations, employment screenings, and even private disputes. But the big question remains, and should they be trusted to uncover the truth? To answer this, it is important to understand how the test works, where it is applied, its legal standing, and the scientific debates surrounding its accuracy.
What Exactly Is a Polygraph Test?
A polygraph test is not a magical truth machine. Instead, it is a scientific instrument designed to measure physiological responses in the body. During a test, the subject is connected to sensors that record changes in blood pressure, pulse rate, breathing patterns, and perspiration levels. The idea is that when a person tells a lie, the body reacts with stress signals, which are then captured on the machine.
In Georgia, polygraphs are commonly referred to as lie detector tests, and they are often administered by certified examiners. The testing process typically begins with a pre-test interview where the examiner explains the procedure and formulates relevant and control questions. Once the examination starts, the subject is asked a series of questions, and the polygraph records the body’s responses. The examiner later interprets the results to determine whether the individual was deceptive or truthful.
While the concept sounds straightforward, the interpretation of these physiological signals is highly complex. Stress, anxiety, nervousness, or even certain medical conditions can affect the results, which is one of the main reasons polygraph tests in Georgia and elsewhere remain controversial.
The Use of Polygraph Tests in Georgia
Polygraph tests in Georgia are used in a variety of settings, each with its own implications and challenges.
- Law Enforcement Investigations: Police departments in Georgia may use lie detector tests during criminal investigations to help identify suspects or verify witness statements. However, the results are usually treated as investigative tools rather than definitive proof.
- Court Cases: Georgia courts rarely admit polygraph evidence because of reliability concerns. Unless both parties in a case agree beforehand, polygraph results are generally not allowed in courtrooms.
- Employment Screenings: Some government agencies and law enforcement employers in Georgia use polygraph examinations to screen potential employees. This is especially common in sensitive positions such as corrections officers, police recruits, and federal jobs.
- Private Disputes: Occasionally, individuals turn to polygraph tests to resolve issues in personal relationships, such as allegations of infidelity or theft. While such uses are voluntary, the accuracy and fairness of results remain debatable.
These different applications highlight the widespread role of lie detector tests in Georgia. However, they also raise important questions about fairness, ethics, and scientific validity.
See also: 7 Natural Healing Practices That Improve Quality of Life
The Legal Status of Lie Detector Tests in Georgia
The legal admissibility of polygraph results is one of the most debated topics surrounding their use. In Georgia, the general rule is that polygraph evidence is not admissible in court. This is consistent with federal standards, which argue that polygraph tests do not meet the threshold of scientific reliability required for evidence.
That said, there are exceptions. In some cases, if both the defense and prosecution agree to accept polygraph results as evidence, a Georgia court may allow them. This scenario, however, is rare.
In employment, the Employee Polygraph Protection Act (EPPA) prohibits most private employers from using lie detector tests during hiring or disciplinary decisions. However, government agencies and law enforcement bodies in Georgia are often exempt from this rule. For example, police departments regularly require candidates to undergo polygraph screenings as part of the hiring process.
Thus, while polygraph tests in Georgia have practical uses, their legal authority is severely limited, reflecting widespread doubts about their reliability.
How Accurate Are Polygraph Tests?
One of the biggest challenges when discussing lie detector tests is their accuracy. Supporters of polygraph testing claim that, when administered properly by trained professionals, the accuracy rate can be as high as 80–90%. Critics, however, argue that results are often skewed by human interpretation and external factors, which reduces reliability to nearly 50%—barely better than chance.
The core issue is that polygraphs do not actually detect lies. Instead, they measure physiological arousal, which is then assumed to indicate deception. But fear, stress, or nervousness can produce the same physiological signals as lying. Likewise, a skilled liar or someone who has practiced countermeasures may be able to suppress stress responses and “beat” the test.
In Georgia, polygraph examiners often undergo specialized training, which may improve the consistency of results. Still, even the most experienced examiners cannot eliminate the underlying flaws of the technology.
Scientific and Psychological Criticisms
Polygraph tests have faced extensive criticism from the scientific and psychological communities. The American Psychological Association has repeatedly stated that there is little evidence to support the claim that polygraphs can accurately and consistently detect lies. Instead, they argue that the test is more of an interrogation tool than a reliable scientific instrument.
Another issue is examiner bias. Since the interpretation of results involves a degree of subjectivity, personal judgment can influence the outcome. In Georgia, as in other states, this subjectivity raises concerns about fairness—especially when the test results can influence job opportunities or criminal investigations.
Psychologists also highlight the placebo effect of polygraph testing. Sometimes, the mere belief that a lie detector test can reveal the truth makes subjects more likely to confess or reveal information, regardless of the actual machine’s accuracy.
The Role of Polygraphs in Georgia’s Criminal Justice System
Despite their limitations, polygraph tests in Georgia continue to play a role in criminal justice. Police investigators often use them to guide questioning or to apply pressure on suspects. For example, a suspect who agrees to take a lie detector test and “fails” may be treated as less credible, even if the results are not admissible in court.
Defense attorneys sometimes recommend their clients voluntarily undergo a polygraph test to demonstrate honesty, especially if results could persuade prosecutors during plea negotiations. While the courts may not accept the results as evidence, they can still influence the direction of a case.
This dual role—both useful and unreliable—creates a paradox in Georgia’s justice system. Polygraphs remain popular despite widespread recognition of their flaws.
Public Perception of Lie Detector Tests in Georgia
Public opinion also shapes the use of lie detector tests in Georgia. Many people believe that polygraphs are nearly infallible, largely due to their portrayal in movies, TV shows, and popular media. This belief sometimes leads individuals to place more trust in polygraph results than the science warrants.
In reality, the test’s reliability is far from guaranteed. Still, because polygraph results can carry psychological weight, they continue to be used as tools for persuasion, intimidation, and negotiation.
Location in Georgia
- Lawrenceville – 1670 McKendree Church Rd, Building 300-B, Lawrenceville, GA 30043
- Roswell – 570 West Crossville Road, Roswell GA 30075
- Oakwood – 4327 Mundy Mill Road, Oakwood, GA 30566
- Atlanta – 3355 Lenox Rd NE, Atlanta, GA 30326
- Newnan – 9 W Broad St, Newnan, GA 30263
- Lilburn – 680 Hillcrest Rd NW, Lilburn, GA 30047
- Savannah – 22 Bull St, Savannah, GA 31401
Alternatives to Polygraph Testing
Given the controversies, researchers have explored alternatives to traditional polygraphs. Technologies such as voice stress analysis, brainwave monitoring (EEG), and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) are being tested as potential lie detection methods. However, none of these have yet achieved widespread acceptance or solved the reliability problem.
For Georgia, this means that polygraphs remain the most common lie detection tool, even though they are far from perfect. Until science produces a more accurate alternative, the debate about polygraph reliability will continue.
Conclusion: Should You Trust Polygraph Tests in Georgia?
So, how reliable are polygraph tests in Georgia? The answer is complicated. While lie detector tests can provide useful insights and sometimes prompt confessions, they are not foolproof indicators of truth. Their accuracy is limited by human interpretation, psychological factors, and the fact that they measure stress rather than lies.
In Georgia, courts generally do not admit polygraph results as evidence, reflecting widespread doubts about their scientific validity. However, they remain popular in law enforcement, employment screenings, and even personal disputes. For now, polygraphs should be viewed as investigative aids rather than definitive truth machines.